The equator is a geographical fiction, which is a line passing through the center of the Earth, perpendicular to the axis of rotation. The main international geographical organizations have adopted the conventional form of the equator in the form of a circle.
It passes exactly in the middle of the Earth and divides the planet into two halves - the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The equator is the most important landmark for navigation - its latitude is 0 degrees, so the measurement of parallels comes from it.
Earth equator geography

We can assume that our planet has the shape of a ball with an average radius of 6371.3 km. But such a representation is not entirely correct and is not always suitable for accurate calculations. If we take scientific concepts and numbers, then the Earth is not an ideal ball, in the world of experts its shape is described by the concepts of a geoid or an ellipsoid.
The imperfect forms of our home planet were discovered back in the distant 17th century by Isaac Newton and Christian Huygens. Due to rotation around its axis and the resulting centrifugal force, which reaches a peak at the equator and zero at the poles, the planet most likely has the shape of a flattened ball. Because of this, the polar radius is less than the equatorial by 21.38 km.
Interesting fact: The Congo River, flowing in Central Africa, is the deepest and second longest on the continent. But the most interesting thing about it is that it is the only river in the world that crosses the equator twice.
The planet reaches its highest rotation speed at zero latitude. This fact can easily be explained by the maximum radius of the Earth at the equator. So equator length is 40075 Km, and if this number is divided by 24 hours (the time during which the planet makes one revolution), then we can find out the speed of rotation of the Earth at zero latitude. Thus, at the equator, it is approximately 1670 km / h. The closer to the poles, the lower the speed.
Equator, Longitude and Latitude
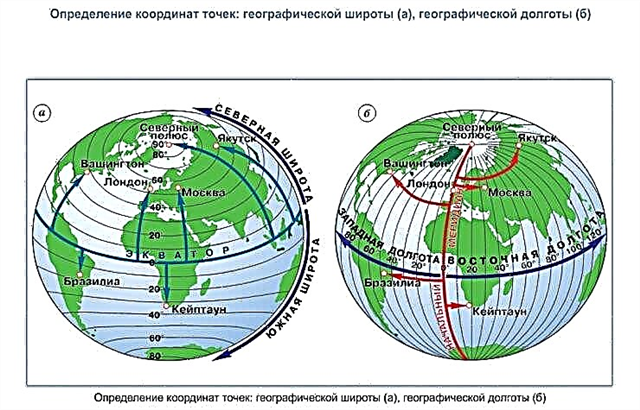
The designation of the equator as latitude is, by definition, 0 °. The Equator is one of the five most important latitudes for navigation, which are considered generally accepted in the geographical community. Four others:
- Arctic Circle;
- Southern Arctic Circle;
- Tropic of Cancer;
- Tropic of Capricorn.
Zero latitude can be considered the only line that falls under the definition of a large circle.
The big circle, in turn, is any circle that passes along the surface of the ball, dividing it in the center. So the equator line runs along the center of the planet, dividing it into two equal halves. Other latitudes cannot be called a big circle, because they, due to their proximity to the poles, do not divide the circle into equal parts.
Parallels, in turn, can be called large circles, since each of them fits the definition. But it is worth considering that the Earth has the shape of an ellipsoid, so the length of any parallel is less than the equator, and accordingly, half are less.
Interesting fact: Brazil has a city called Macapa. It is located simultaneously in two hemispheres. In the center of the city is the football stadium, named after Estadio Milton Correa. The center line of the field of this stadium runs almost exactly along the equator line. Not far from the sports facility is the monument “Marco Zero”.
Territories located on the equator line experience the shortest sunrises and sunsets. This is due to the fact that the daily trajectory of the Sun is almost perpendicular to the horizon for most of the year. The length of daylight hours (from sunrise to sunset) is almost constant throughout the year; it is about 14 minutes longer than nighttime due to atmospheric refraction (refraction of the sun's rays) and the fact that the sunrise is counted from the moment when the upper part, and not the center, of the solar disk is in contact with the horizon.
Climate at the equator

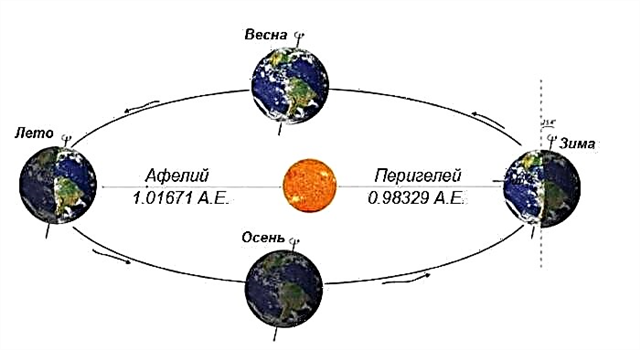
The seasons are the mutual influence of the tilt of the axis of the earth with respect to the plane of its rotation around the sun. Throughout both hemispheres alternately approach the Sun and turn away from it, which primarily depends on the position of the Earth in orbit. The hemisphere that is currently turned closer to the star receives more solar radiation, so it is in the summer season. The hemisphere, which is further from the Sun, on the contrary receives less, therefore it is in the winter stage.
The equator is always located at approximately the same distance from the sun. It passes through the three largest oceans: the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific. A slight change in temperature is observed along the equatorial line throughout the year, although there may be significant differences in precipitation and humidity. The terms summer, autumn, winter and spring are usually not applied to this climate zone.
The lowlands located at the equator tend to have a tropical rainforest climate, also known as the equatorial climate. Although cold currents lead to the fact that in some regions there is a tropical monsoon climate with a dry season in the middle of the year, and the Somali current generated by the East Asian monsoon leads to an extremely dry climate on the territory of the Somali Peninsula, despite its equatorial position.
Interesting fact: some countries got their name from the word “equator”: Ecuador, Equatorial Guinea, Equatorial Africa.
The average annual temperatures in the equatorial lowlands are around 31 ° C in the afternoon and 23 ° C during sunrise. The level of precipitation is extremely high in comparison with the zones farther from the equator - they can reach from 2500 to 3500 mm. There are about 200 rainy days in a year, and the average annual number of hours of sunshine is about 2000. Despite the hot year-round temperature, some points located much above sea level, such as the Andes and Mount Kilimanjaro, have glaciers. The highest point is the southern slopes (4690 meters) of the Kayamba volcano (peak 5790 meters). This is the only place along the equator where you can find snow lying on the surface of the earth.
If you move away from the equator line in any direction, the amount of solar radiation will decrease, which thereby contributes to the formation of other climatic zones. But the stability of weather throughout the year in the equatorial zone has made this area home to a greater diversity of flora and fauna than anywhere else on the planet. It is the forests that grow here are the "lungs of the Earth", producing oxygen, which breathes all life.
Equator countries
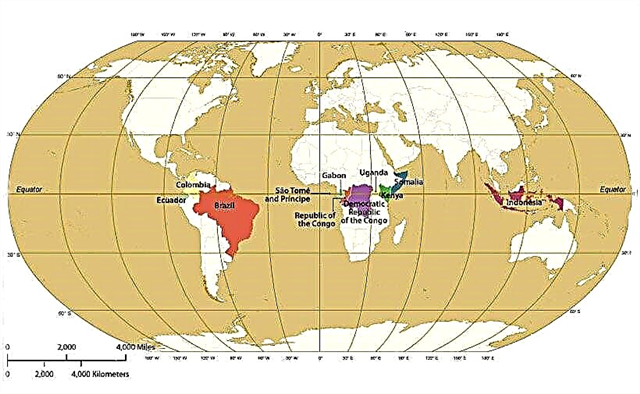
Only 11 states are at the equator. If you take the Zero Meridian as a reference point and move east, then at Zero Latitude are:
- Sao Tome and Principe;
- Gabon;
- Republic of the Congo;
- Democratic Republic of the Congo;
- Uganda;
- Kenya;
- Somalia;
- Indonesia;
- Ecuador;
- Colombia;
- Brazil.
You can also add two countries along the territorial sea of which the equator line passes, but does not directly affect land:
- Maldives;
- Kiribati.
The Equator is the best starting point for space flights, and accordingly for the construction of spaceports, for example, the Guiana Space Center, which is located in the capital of French Guiana. Such cosmodromes get a great advantage due to the use of the natural rotation of the celestial body - the additional speed reduces the amount of fuel that is required to put the device east (in the direction of planet rotation) into orbit, while avoiding the costly maneuvers that have to be resorted to to smooth the inclination start time. [/ tds_note]












